Hyper-V server hardware requirements
Jump to:
Hyper-V is a tool that allows you to create and run multiple independent virtual machines on a single physical server. This can also be referred to as server virtualization technology. In this article, we will tell you what it is and why businesses need it.
How virtualization works
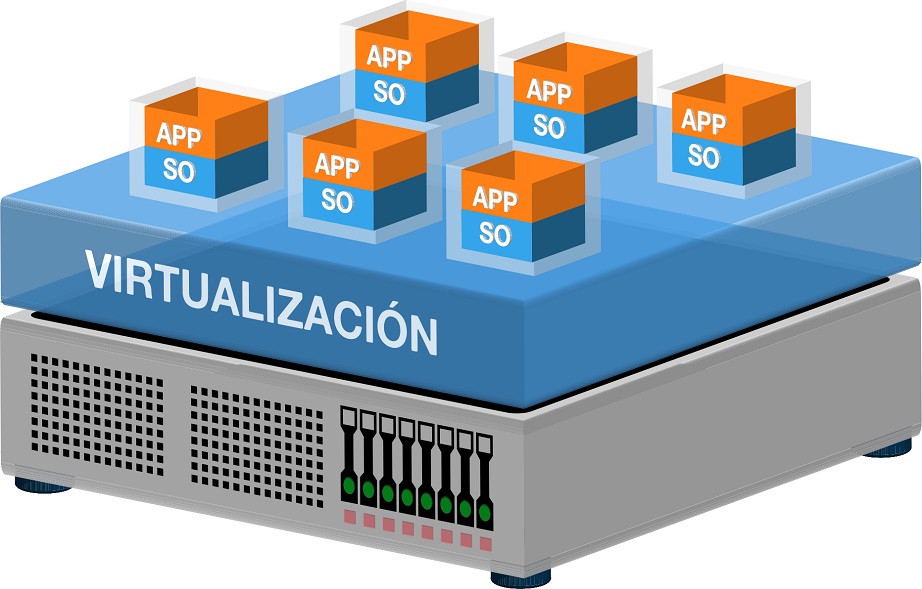
Virtualization is the software partition of a server (host) into several virtual machines(guests) capable of functioning in isolation from each other. It is based on a hypervisor - a kind of conductor between the host and the virtual machines.
Hypervisors come in several varieties:
-
Type I hypervisors are hardware or bare-metal hypervisors that run directly on the host machine hardware. Examples: VMware ESXi, Citrix XenServer.
-
Type II hypervisors are host-based hypervisors that run on top of the underlying operating system installed on the host server. Examples: VMware Workstation,Oracle VirtualBox.
-
Another type that is classified separately is the hybrid type, which combines features of the first and second type. Such hypervisors run on bare-metal hardware, but some kind of control operating system is required to manage it.
The Hyper-V hypervisor belongs to the latter type. The main advantages of such programs are their high security and high performance, since there is no layer between the software and the processor vulnerable to being attacked and hacked.
Why server virtualization is needed
The Hyper-V platform was developed by Microsoft and was first introduced in 2008. With it you can run multiple virtual machines on a single server. This helps to optimize company resources through intelligent use of hardware and to build scalable,fault-tolerant systems that are easy to manage and maintain.
Let us explain with a simple example:
Company X uses two physical servers: one for file storage and FTP, the other for terminals. Since the load in this case is non-linear, some equipment capacity is periodically idle. On the other hand, company Y purchased only one, but more powerful server, and used virtualization, distributing the load between virtual machines.
As we can see, the hypervisor takes the surplus where it is not needed and transfers it to where there is a shortage. This reduces electricity and cooling costs and saves on hardware purchases.
Virtualization also allows you to:
-
Run several stand-alone systems that do not affect each other on a single server.
-
Create an isolated software environment for any user by defining an individual list of programs allowed to run.
-
Create a virtual and therefore flexible infrastructure for the company.
Thanks to Hyper-V, clients can run different operating systems on the virtual machine: Linux, FreeBSD and Windows. Thus, every company can build its own virtual environment that will fully meet its needs and objectives.
How Hyper-V can help you at work

Hyper-V comes in three variants:
-
As a component of Windows, a direct analog of VMware Workstation and similar systems. It is also used for technologies such as WSL2.
-
As a component of Windows Server, necessary for building a virtual infrastructure.
-
A separate free version of Hyper-V Server, which is the base version of Windows Server Core, including full Hyper-V functionality, while other Windows Server roles are not available, including the graphical shell.
The main function of Hyper-V is to quickly create and configure virtual machines.However, the server version has other useful features worth mentioning:
-
PowerShell Direct. An important option that allows you to connect to a virtual machine for remote management without requiring network access to the guest operating system.
-
Clustering. Clustering provides system fault tolerance by moving workloads from one virtual machine to another in case of failure.
-
Control points. One of the major benefits of virtualization is the ability to easily save the state of a virtual machine and move backwards or forwards at a given point in time if necessary. In Hyper-V, this feature is called a virtual machine checkpoint. The software uses several types of checkpoints: standard checkpoints that take a snapshot of the state of the virtual machine and virtual machine memory at the time the checkpoint is created, and production checkpoints that use volume shadow copying.
-
Nested virtualization. Hyper-V also allows you to create a virtual machine inside a virtual machine and test different scenarios: create a virtual host or run Hyper-V or Windows Sandbox containers on a virtual machine.
Minimum system requirements for Hyper-V on a Windows server

Hyper-V has certain hardware requirements, and the more extra features you use, the higher the requirements you will have to meet. The minimum hardware specifications are as follows:
-
64-bit processor with second level address translation (SLAT).
-
Support for virtual machine monitoring mode (VT-x technology on computers with Intel processors).
-
At least 4 GB of RAM.
The following components must be enabled in the system BIOS:
-
Hardware virtualization (Intel VT or AMD-V).
-
Hardware data execution prevention with the NX bit for AMD systems or the XD bit for Intel systems.
To check your hardware and operating system compatibility with Hyper-V, open the Windows PowerShell console or command line (cmd.exe) and run the system info command. If all of the above mentioned points are marked "Yes", the system supports Hyper-V. If at least one item is marked "No", you need to recheck the requirements and make the necessary adjustments.
IMPORTANT: Only 3-4 basic virtual machines can run on a host with a minimum of 4 GB of RAM. Running larger numbers of machines or complex programs will require more resources.
3 Best Hyper-V Server
Our guys at Servermall can help you choose the right equipment. Below are a few popular options that can be configured to your specific business needs:
-
DELL PowerEdge R730xd. The versatile Dell 13th generation platform, featuring an excellent price/performance ratio, supporting up to 12 3.5" drives with a diskless configuration option.
-
HPE Proliant ML350 Gen9. For those who prefer Tower form factor servers, here is a relatively inexpensive option that allows you to install up to 8 drives 2.5 inches, plus configuration options.
-
DELL PowerEdge R740. An excellent higher-end model, suitable for building high-load hyperconverged infrastructures - up to 24 2U drives.
Any of the servers in our catalog can be customized by replacing practically any component with the one you need. All models also come with a 5-year warranty and free shipping.
Choice of equipment

Hyper-V virtual machines require more resources due to server consolidation. If you plan to select your hardware yourself, consider the following features:
-
The server and each individual virtual machine require a processor capable of supporting Second Level Address Translation technology (SLAT). Special consideration is needed for the number of cores associated with the planned number of virtual machines.
-
The processor clock frequency is selected depending on the planned load.
-
Minimum host system RAM is calculated according to the recommendations, anything on top is based on the number of virtual machines.
-
Storage type should be chosen depending on the planned architecture: converged, hyperconverged or just standalone servers.
-
It is desirable to install a network adapter of at least 10Gbps with RDMA support, especially if you plan to build a hyperconverged infrastructure.
-
A large CPU cache will have a positive effect on performance. This is important to consider for workloads with a large working set in memory and in virtual machine configurations where the ratio of virtual processors to logical processors is high.
-
Sufficient I/O capacity and bandwidth is also important for storage equipment when it comes to standalone servers. You should keep this in mind when selecting controllers, storage disks and RAID configurations. Placing virtual machines with resource-intensive workloads on different physical disks can improve overall performance. For example, if four virtual machines are using one disk and are actively using it, each virtual machine can deliver about a quarter of the bandwidth of that disk.